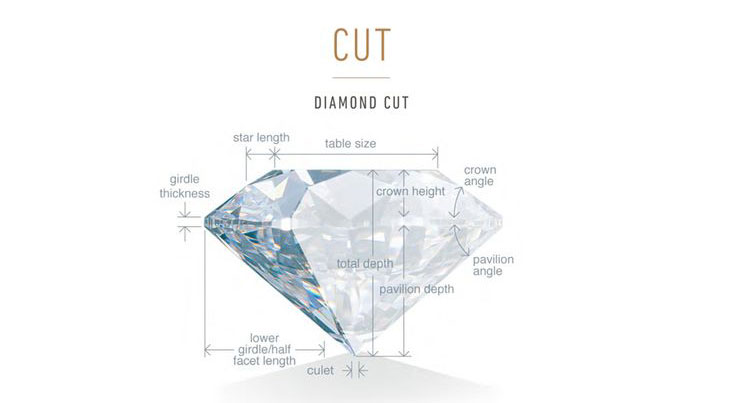
What Are The Four C's?
The "4 Cs" are four distinct characteristics that determine the quality of a diamond. Like a finger print, no two diamonds are exactly alike. Until the middle of the twentieth century, there was no agreed-upon standard by which diamonds could be judged. GIA created the first accepted standard for describing diamonds: Colour, Clarity, Cut and Carat weight.